Traffic bottlenecks at toll booths may seem like a thing of the past — until you're stuck in one. Despite all the advancements in transport tech, many toll roads still deal with long queues, manual intervention, or unreliable systems. That’s because the real enablers of fast, seamless tolling — technologies like RFID and GPS — often don’t reach their full potential.
Why? Because the impact of any technology depends not just on what it can do, but on how well it’s integrated into a larger system.
In this blog, we’ll break down how RFID and GPS work in toll collection, explore their benefits, and explain how automatic toll collection systems make the most of them.
A quick look at electronic toll collection systems (ETC)
Before we dive into the tech itself, let’s get familiar with the framework these technologies operate within.
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) refers to systems that allow vehicles to pass through toll points without stopping.
These systems automate the identification and payment process using technologies like RFID tags, license plate recognition, or GPS-based tracking.
Here’s how it works:
- A vehicle is identified through a unique ID, either through an RFID tag or its real-time GPS position
- That ID is matched to a user account with sufficient balance or a linked payment method
- The system deducts the toll fee instantly and records the transaction in real time
Why does this matter? It’s because ETC reduces congestion, improves road safety, and helps toll operators like you manage resources more efficiently. It also makes the experience faster for drivers
Besides, it becomes more manageable for you, but only when the underlying technologies perform reliably.
RFID in automatic toll collection systems: What is it, and how does it work at toll booths?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is one of the most widely used technologies in toll operations. Here's how it works:
- An RFID tag is placed on the windshield of a vehicle
- As the vehicle approaches the toll booth, a reader installed overhead or at the side picks up the signal
- The system identifies the vehicle, checks for toll eligibility, and deducts the amount—all in a matter of seconds
- The barrier lifts, and the vehicle moves through without stopping
It’s this kind of speed and automation that makes RFID a go-to choice for fixed-location toll plazas.
Real-world use cases of RFID in tolling
Globally, RFID is a proven technology for large-scale electronic toll collection systems. Examples include:
- FASTag in India: It’s a nationwide RFID-based ETC system that’s mandatory for all vehicles on national highways
- E-ZPass in the United States: It covers multiple states across the Northeast, Midwest, and South
- Urban toll plazas, expressways, dedicated freight corridors, and bridges all increasingly rely on RFID for smoother operations
RFID works in both open-loop systems (where payment is processed through banks or wallets) and closed-loop systems (where toll payments are processed entirely within the operator’s ecosystem).
Key benefits of RFID technology in toll operations
RFID isn’t just fast; it brings tangible operational and financial benefits.
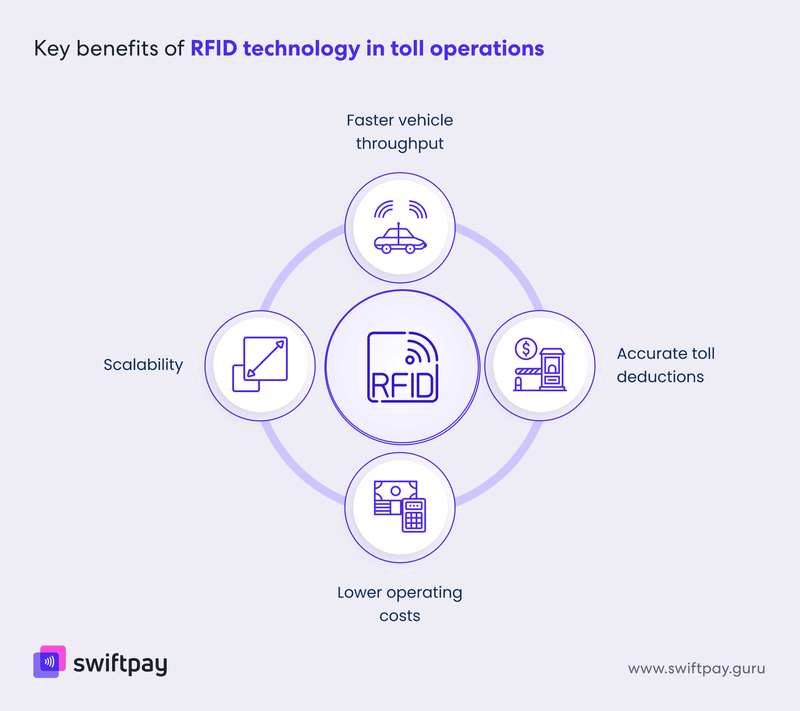
Faster vehicle throughput
With RFID, vehicles don’t need to stop — or even slow down significantly — to pay tolls. This helps prevent long queues and supports smoother traffic flow.
Accurate toll deductions
Because each vehicle is uniquely identified and tracked, toll deductions are more accurate and easier to verify. This reduces the chance of disputes or manual errors.
Lower operating costs
Less manual processing means lower labor and maintenance costs. RFID-based booths also face fewer breakdowns or disruptions.
Scalability
RFID systems are highly scalable, making them ideal for closed-loop tolling setups where the operator has full control over the ecosystem.
GPS in automatic toll collection systems: What is GPS-based tolling, and how does it work?
GPS-based automatic toll collection systems bring automation to routes where toll booths don’t make sense or are hard to implement.
Here’s how it works:
- Vehicles are equipped with GPS-enabled devices or telematics units
- Their movement is tracked in real time
- When a vehicle enters a predefined toll zone or completes a certain route, toll charges are calculated based on distance, time, or entry/exit points
- The toll is then deducted from a user account automatically
This model is especially useful for long-haul trucking, intercity travel, and areas where infrastructure costs for physical toll booths are too high.
Real-world use cases of GPS tolling
Several countries have successfully implemented GPS-based electronic toll collection systems:
- Germany uses GPS to toll heavy commercial vehicles across its national highway network
- Singapore is transitioning to a satellite-based ERP (Electronic Road Pricing) system
- GPS tolling is also being explored in parts of Europe, the U.S., and Asia for distance-based pricing and dynamic congestion management
These systems often integrate with smart city platforms, traffic control systems, and commercial fleet management tools.
Read more: How Toll Collection Systems Can Help Optimize Fleet Efficiency
Key benefits of GPS in toll operations
While not every toll setup can use GPS, its benefits are clear for certain use cases.
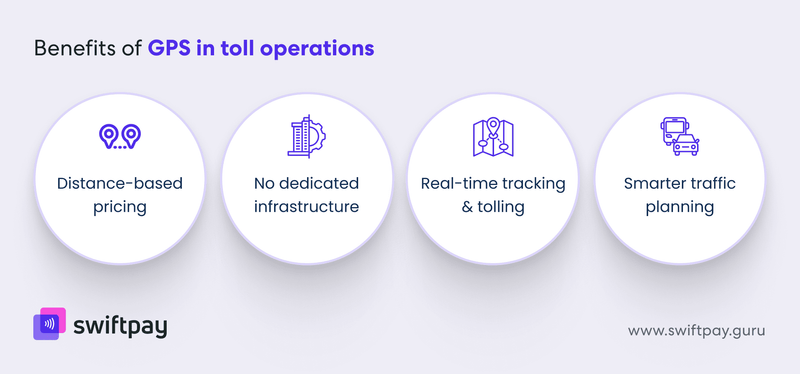
Distance-based pricing: more flexible and fair tolling
GPS allows for tolls to be charged based on how far a vehicle travels, not just entry and exit points. This supports fairer, usage-based billing.
No need for physical toll booths
With GPS, there’s no need for fixed infrastructure. This is ideal for rural roads, remote expressways, or expanding regions where booth setup isn’t feasible.
Real-time tracking & tolling
For fleets, GPS tolling can be integrated with telematics to manage toll costs dynamically, track vehicle routes, and improve route planning.
Supports broader traffic and mobility planning
By collecting rich vehicle movement data, GPS-based ETC systems give you deeper insights into traffic patterns, congestion zones, and road usage. You can use these insights to make smarter infrastructure decisions.
How SwiftPay simplifies automated toll collection
At this point, it’s clear that both RFID and GPS play a major role in making automatic toll collection faster and more efficient.
But even the best technology needs the right system behind it to truly perform.
That’s where SwiftPay comes in.
SwiftPay is a closed-loop automatic toll collection system designed for high-speed and low-friction toll environments powered by RFID.
Here’s how SwiftPay can ease your toll operations:
Built for speed and stability
SwiftPay uses RFID to process toll payments instantly, even in areas with limited internet connectivity. Since it doesn’t rely on external banks or wallet APIs, it eliminates the risk of transaction delays or failures.
Full control for toll authorities
As a closed-loop platform, SwiftPay gives toll operators like you full ownership of the system. You can define pricing rules, configure exemptions, and set business logic. All of that without needing third-party approvals or bank integrations.
Smarter data & smoother operations
SwiftPay includes real-time dashboards, vehicle tracking logs, and transaction reports. All these can help you manage operations more intelligently and plan for future growth.
Final words
RFID and GPS have revolutionized toll collection, no doubt about it. RFID brings unmatched speed to booth-based tolling. GPS enables dynamic, infrastructure-free tolling on broader roads.
But without a system that brings reliability, control, and real-time visibility, these technologies can fall short.
SwiftPay aims to bridge that gap.
It gives toll operators like you a fast, secure, and flexible way to implement an RFID-based automatic toll collection system, without relying on outside networks or payment providers.
If you're looking to modernize your toll operations, start with the system that makes your technology work better, not harder.